The gig economy has emerged as a transformative force in the global labor market, reshaping how people work and earn a living. Characterized by short-term contracts, freelance work, and flexible employment arrangements, the gig economy is driven by technological advancements and evolving workforce expectations. This article delves into the key aspects of the gig economy, its benefits, challenges, and implications for workers, businesses, and policymakers.
What Is the Gig Economy?
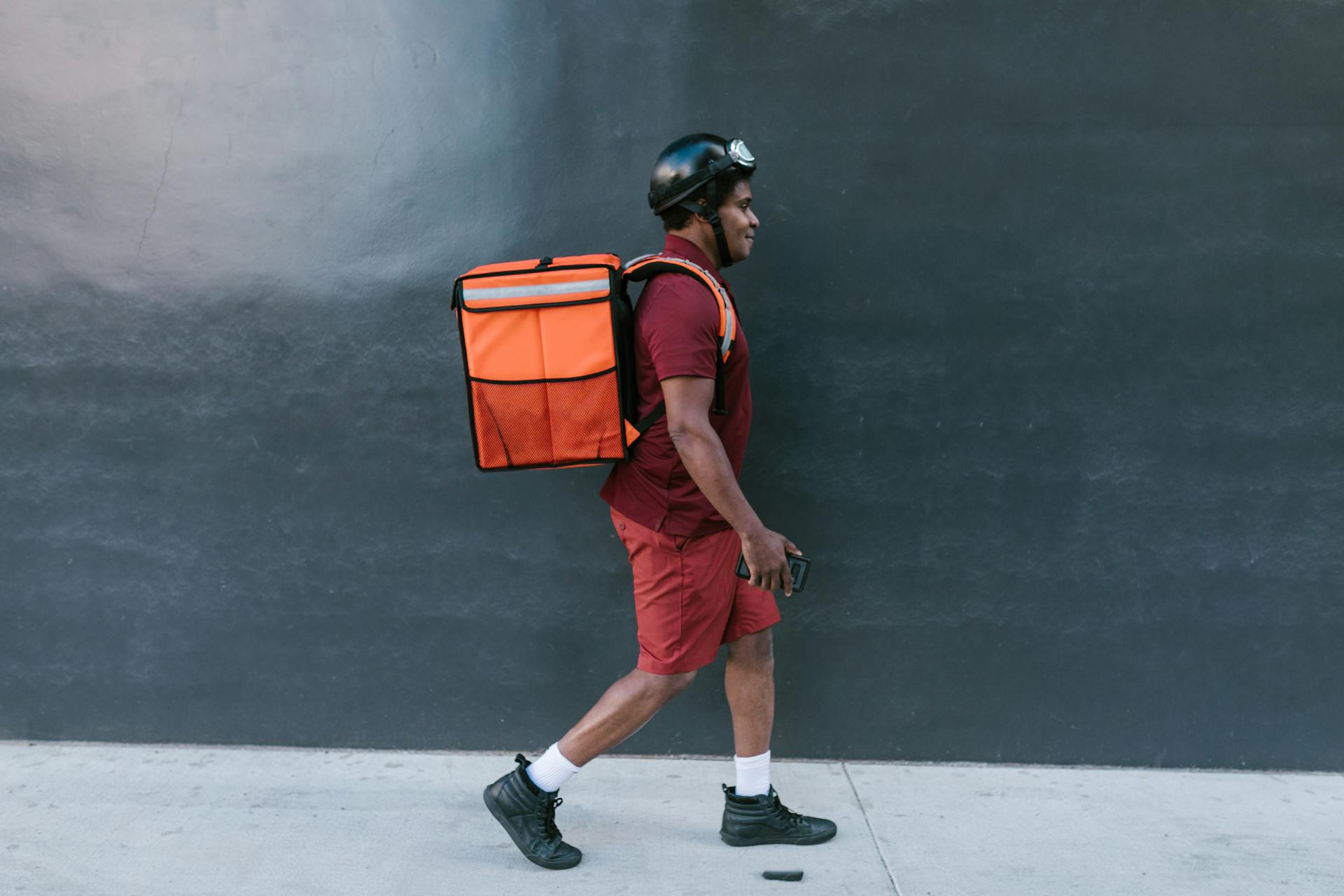
The gig economy refers to a labor market where temporary, flexible jobs are the norm. Workers engage in gigs, which are short-term tasks or projects, rather than traditional full-time employment. Platforms like Uber, Upwork, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit have become hallmarks of this economy, connecting gig workers with clients or customers.
The rise of digital platforms and mobile apps has been instrumental in expanding the gig economy, allowing individuals to work on-demand, often from remote locations. From delivering food and driving passengers to designing websites and writing content, gig opportunities span a wide range of industries and skill levels.
Benefits of the Gig Economy
1. Flexibility and Autonomy
One of the most significant advantages of gig work is the flexibility it offers. Gig workers can choose when, where, and how they work, tailoring their schedules to fit their personal and professional goals. This autonomy appeals particularly to individuals seeking work-life balance, such as parents, students, or retirees.
2. Diverse Income Streams
Gig work allows individuals to diversify their income sources. Many use gig platforms as a supplementary income stream while pursuing other career or personal endeavors. This diversification can provide financial security and reduce dependence on a single employer.
3. Lower Barriers to Entry
For many gigs, the entry requirements are minimal, enabling people from diverse backgrounds and skill levels to participate. For example, a driver with access to a car can begin working for a rideshare platform with relative ease, while a skilled graphic designer can find freelance projects online without the need for a traditional employer.
Challenges of the Gig Economy
1. Lack of Job Security
Gig workers often lack the job stability associated with traditional employment. They are classified as independent contractors, which means they do not receive benefits such as health insurance, paid leave, or retirement contributions.
2. Income Volatility
While the gig economy offers income opportunities, earnings can be unpredictable. Gig workers face fluctuations in demand, competition, and platform policies, which can affect their financial stability.
3. Legal and Regulatory Issues
The gig economy’s rapid growth has outpaced the development of regulations. Issues such as worker classification, taxation, and fair compensation are ongoing challenges for policymakers, businesses, and workers.
Implications for Stakeholders
For Workers
To thrive in the gig economy, workers must develop strong self-management skills, diversify their skills, and stay informed about their rights and responsibilities. Building a financial cushion to manage income fluctuations is also essential.
For Businesses
Companies leveraging gig workers benefit from reduced labor costs and access to a global talent pool. However, they must balance these advantages with ethical considerations and compliance with evolving labor laws.
For Policymakers
Policymakers must address the gig economy’s regulatory gaps by developing frameworks that protect workers’ rights while fostering innovation and economic growth. Ensuring fair compensation, social protections, and equitable taxation will be critical.
Conclusion
The gig economy represents a paradigm shift in how work is conceptualized and executed. While it offers flexibility, opportunities, and innovation, it also poses significant challenges that require thoughtful solutions. By addressing these issues collaboratively, workers, businesses, and policymakers can unlock the full potential of the gig economy while ensuring its sustainability and inclusivity.